23 Jun 2025
11 MIN READ
Three Unique Republics of Russia – Buryatia, Yakutia, and Dagestan
Summary
The Russian Federation has 21 Republics. They are semi-autonomous regions with their constitutions, official languages (in addition to Russian), and varying degrees of self-governance. Some of them are typically home to specific ethnic groups.
Buryatia, Yakutia, and Dagestan are key examples. These three republics are among Russia's most unique regions. They are not what people think of as “typically Russian” with their distinctive indigenous cultures.
Russian soviet republics compared to post-1991
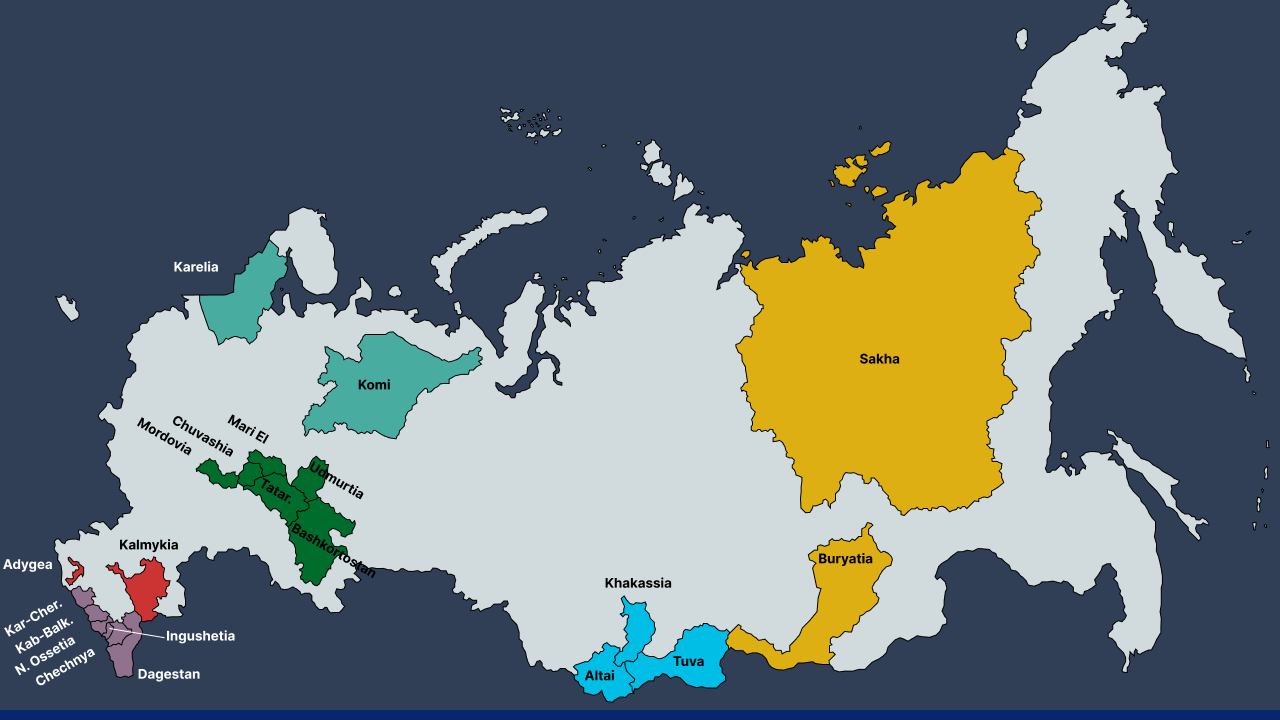
Republics of Russia – Buryatia, Yakutia, and Dagestan. Credits: Wikipedia
From 1922 to 1991, Russia was part of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), with several autonomous republics. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, many regions became the republics of modern Russia.
The RSFSR had approximately 16 to 20 autonomous republics, which were referred to as Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics (ASSRs). They were designed to represent different ethnic groups. They had limited autonomy but were controlled by the Soviet Union.
In modern-day Russia, the republics have constitutions, official languages, and governors. While the republics have some autonomy, it is limited. Moscow still exerts firm control over their policies and leadership.
The Republic of Buryatia, Russia
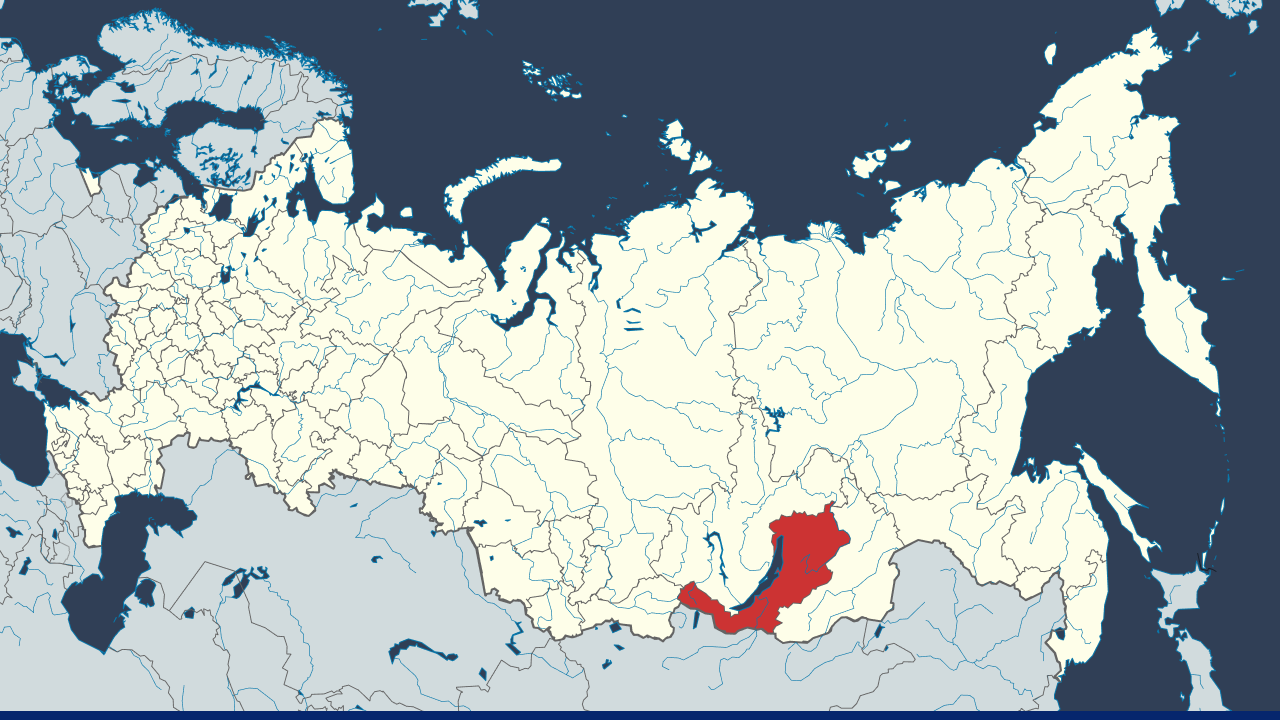
Location of the Republic of Buryatia. Credits: Wikipedia
What is the Geography & Location of the Republic of Buryatia?
Buryatia, also known as the Republic of Buryatia, was formerly part of the Siberian Federal District. It was founded in 1923 and covers a total area of 1,25,637 square miles. It is a federal subject of Russia located in southeastern Siberia.
The Republic of Buryatia lies along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal, the world’s deepest freshwater lake, and borders Mongolia to the south. The republic has a population of just under a million, and its capital and largest city is Ulan-Ude.
History of the Buryats
The Buryats are believed to have originated from the Mongolic-speaking tribes that inhabited the region around Lake Baikal in Siberia. Some experts believe that they are the descendants of the Xianbel and Khitan people.
In the 18th century, the Russian Empire had established control over the Buryat lands. However, after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Republic of Buryatia was established as a federal subject of Russia with a high degree of autonomy.
What is the cultural identity of the Republic of Buryatia?
Buryatia is home to the Buryats, a Mongolic ethnic group. The Buryats' rich cultural heritage blends Indigenous traditions with Mongolian and Tibetan Buddhist influences. Buddhism, along with traditional shamanism, plays a central role in the spiritual life of the Buryats. Historically, the Buryats were a nomadic people related to Mongolians.
Buryat customs emphasize the importance of welcoming guests, a tradition rooted in their historic nomadic heritage. Nomadic cultures rely on mutual support and hospitality in the harsh Siberian climate. Generosity is a virtue in these societies.

Celebration of Surkharbaan, Buryats' main summer festival. Credits: Pavel Kuzmichev, Gateway to Russia
Attractions in the Republic of Buryatia
Lake Baikal is Buryatia's key attraction. It is a sacred place for Buryats. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1996, protected for its unique ecosystem and cultural significance.
Buryatia’s capital, Ulan-Ude, is home to one of the most famous Buddhist sites, the Ivolginsky Datsan, a monastery located near Ulan-Ude. It attracts pilgrims from across the region. The city is also renowned for having the most prominent head statue of Vladimir Lenin.
Key issues in the Republic of Buryatia
Buryatia faces economic struggles, including high unemployment and underdeveloped infrastructure. Many young people leave for larger cities in search of better opportunities. However, they are often discriminated against when they apply for jobs and apartments in cities like Moscow.
Even to this day, many apartment advertisements say, ‘For Slavic tenants only,’ which discriminates against not only Buryats but also other Russians from the East, such as Yakutia and Central Asian migrants.
Major issue faced in the Republic of Buryatia today
One major issue is the region’s economic dependence on Moscow. Despite its rich natural resources, Buryatia remains economically underdeveloped, with high unemployment and low wages. Buryatia has one of the highest poverty rates in Russia.
This has fueled dissatisfaction, leading some Buryats to call for greater autonomy. However, the Russian government heavily suppresses any push for regional independence, which maintains tight control over its federal subjects.
The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Russia
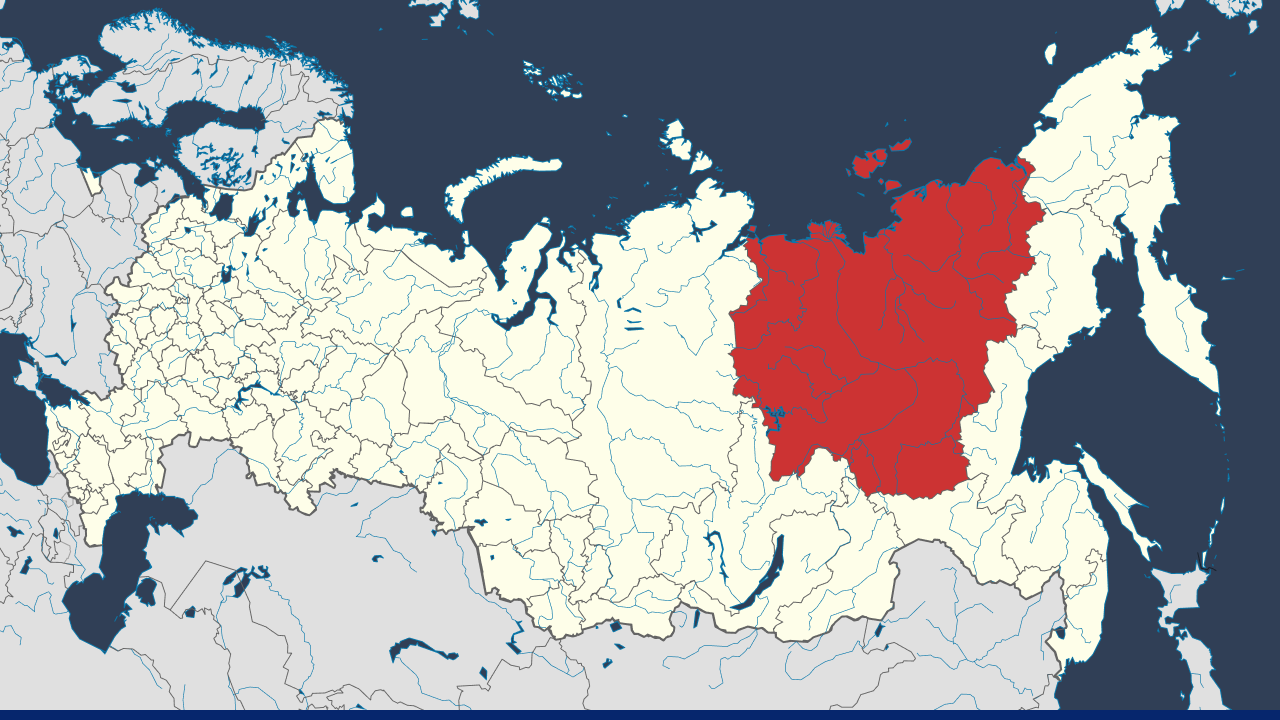
Location of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). Credits: Wikipedia
What is the geography & location of the Republic of Sakha?
Yakutia, also known as the Republic of Sakha, is located along the Arctic Ocean, in the Northeast of Russia. It is the largest in Russia and one of the most sparsely populated regions. Its area is about the same size as India, just over 3 million square kilometers. However, its population is only around a million.
It is famous for its freezing climate, the coldest part of the world. Temperatures can drop as low as -58°F/-50 °C, sometimes much lower, into the minus 70s.
History of Yakutia
It is believed that the Sakha people came from a mix of local Siberian and Turkic migrants between the 6th and 10th centuries CE. They were originally semi-nomadic people who lived along the Lena River.
During that period, the Sakha people were included in the Russian Empire and founded Yakutsk in 1632. By the 17th century, they were organized into 80 independent tribes. Further Russian colonization led to increased settlement, leading to cultural changes and a shift toward sedentary farming.
What is the cultural identity of the Republic of Sakha?
Just over half of the population consists of Yakuts, the indigenous people of the region. They are very distantly related to other Turkic people in Central Asia. About 35 percent of the population is ethnic Russians.
The remaining population comprises other indigenous ethnic groups in Russia, such as the Evenk and Lamut.
Some important sites of the Republic of Sakha
The Republic of Sakha's capital city is Yakutsk, the coldest city in the world. The Permafrost Kingdom is outside the city center, a unique ice museum situated within permanently frozen tunnels. It features neon-lit ice sculptures of gods, historical figures, and famous artworks, and it remains frozen year-round. Yakutsk’s permafrost has a significant impact on daily life, affecting both infrastructure and the local climate. Located 13 km from the city center, it’s a must-visit attraction.
Oymyakon is another key attraction in Yakutia. It is a small village of about 2,000. That holds the record for the coldest inhabited place on Earth. This remote village faces extreme conditions. Its residents breed livestock and endure harsh winters. Despite the challenges, Oymyakon remains a symbol of resilience.
The Lena Pillars are a key site in Yakuria. It is a UNESCO Heritage Site as it is a geological and ecological landmark. The Lena Pillars feature towering 100-meter rock formations along the Lena River. Extreme climate fluctuations and freeze-thaw erosion formed them. These pillars support Cambrian fossils that are over 500 million years old.

Lena, Pillars, Yakutia. Credits: VasilyevaED, Wikimedia
What are the key issues in the Republic of Sakha?
Similar to other unique regions in Russia with indigenous populations, Yakutia struggles to balance its culture with Russianization. While its language is recognized and used, Russian is the dominant language in government and education.
Yakutia is rich in many natural resources, including diamond and gold deposits. However, much of the profits often go to Moscow instead of the region. The economic situation in Yakutia is less than desirable. Many Yakuts have to leave to work in other Russian cities. Similar to the Buryats, they face a lot of institutional racism in cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Many remote areas struggle with a lack of infrastructure and access to healthcare. The environment is too hostile to make significant progress in expanding infrastructure. The hostile weather contributes to a lot of mental health problems. Yakutia has a high suicide rate, and many struggle with alcoholism.
Republic of Dagestan, Russia

Map of Dagestan. Credits: Wikipedia
What to know about the Republic of Dagestan?
The Republic of Dagestan is located in the North Caucasus region of southern Russia, bordered by the Caspian Sea to the east. It shares borders with Azerbaijan and Georgia. Dagestan has a mountainous terrain in the Caucasus Mountains.
The capital city is Makhachkala, located along the Caspian Sea coast. Its capital is the only Russian city named not after a specific group in Dagestan, due to the large number of ethnic groups.

Republic of Dagestan Parliament, Makhachkala, Dagestan. Credits: Igor Puh
What is the cultural identity of the Republic of Dagestan?
The Republic of Dagestan is Russia's most ethnically diverse region, with representatives of various nationalities and ethnic groups. The region is often described as a "melting pot" of different cultures. Many ethnic groups have coexisted for centuries, maintaining a strong sense of regional and clan identity.
The most common ethnic group is the Avar, which comprises approximately 30% of the population of the Republic of Dagestan. The other largest groups are Dargin, Kumyk, and Lezgin. There are many more in the single digits of percentage. Ethnic Russians only account for about 3%. Islam is the most widely practiced religion in Dagestan. Islamic practices influence much of the cultural life.
Key attractions of the Republic of Dagestan
Dagestan has some of Russia’s most breathtaking landscapes. Located in the Caucasus Mountains, it has the Sulak Canyon, the deepest in Europe, carved by the Sulak River. It is deeper than the Grand Canyon. Dagestan is home to the UNESCO site of Derbent, famous for its fortress. Many also visit the historic Gunib and Chokh, a mountain village.
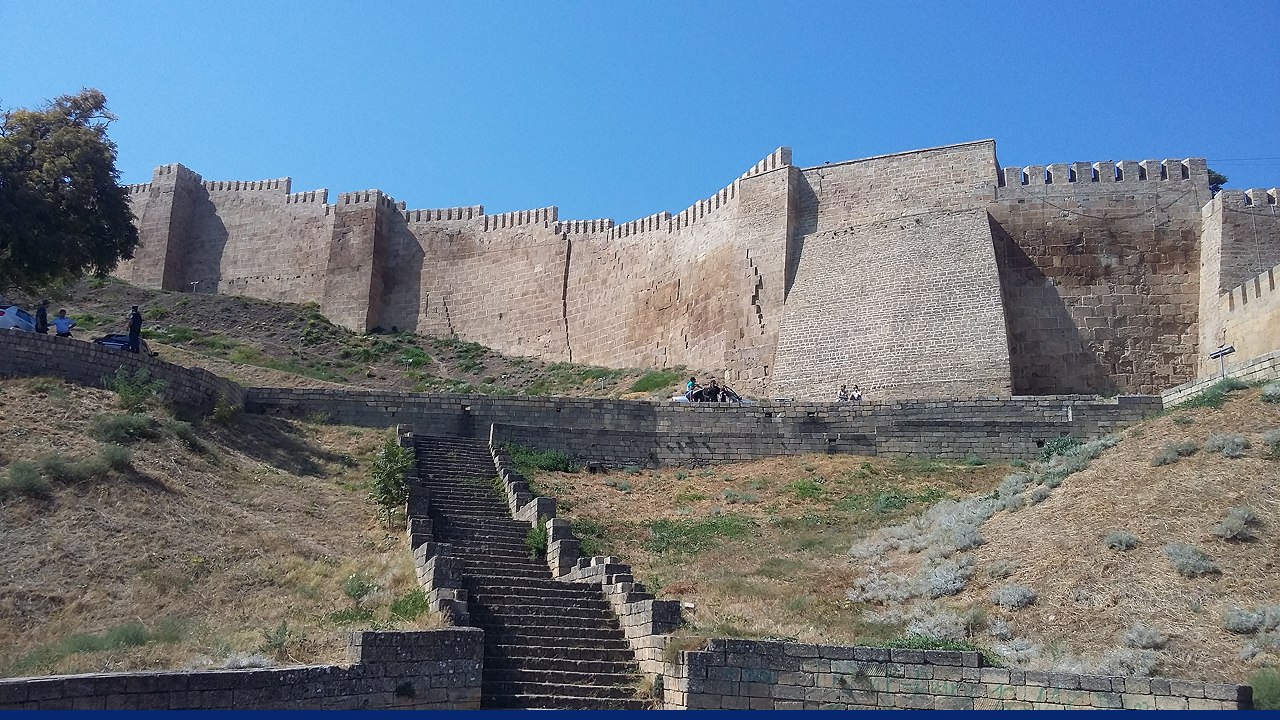

Fortress in Derbent, a UNESCO heritage site. Credits: Igor Puh
Gamsutl, a ghost town, is another key attraction, often referred to as Russia’s Machu Picchu. It is at an altitude of almost 1,500 meters in the Caucasus Mountains. It was an Avar village, carved out of rock, dating back approximately 2,000 years.
What are the key issues in the Republic of Dagestan?
Dagestan has one of the highest unemployment rates in Russia. Many residents struggle to find stable employment, which contributes to poverty in rural areas, particularly in mountainous regions. Like Yakutia and Burytia, many people have moved to other parts of Russia or abroad. The area's lack of prospects jade the youth.
Mass mobilization for the Ukraine war has also hit Dagestan at higher rates than other Russian Republics. Soldiers from Dagestan have died at a rate 10 times higher than in Russia. Dagestan's ethnic diversity has led to interethnic tensions. Frequent clashes between ethnic groups drive competition for resources, influence, and political power.
Conclusion
These three republics (Buryatia, Yakutia, and Dagestan) highlight the vast culture and ethnic diversity within Russia’s republics, and each has its unique identity. Despite their rich cultures, traditions, and natural resources, all three republics face high unemployment, limited infrastructure, and strong central control from Moscow.
Many people migrate in search of better opportunities and end up facing discrimination elsewhere in Russia. However, their resilience and histories continue to shape and enrich the Russian Federation.
People also ask
What are the different republics of Russia?
The 22 republics of Russia are autonomous regions that serve as the homeland for specific ethnic minorities and have their own constitutions, as well as official languages (in addition to Russian). However, they only enjoy some degree of autonomy.
Which parts of Russia want independence?
Several regions in Russia have independence movements, although their strength and popular support vary widely, ranging from secession to autonomy for certain federal subjects or areas within the Russian Federation.
What are the republics of Siberia?
Siberia has several republics that are part of the Russian Federation. These republics are home to various indigenous peoples and ethnic minorities, many of whom maintain distinct languages and cultural traditions.
What are the different types of Russia?
Russia has a diverse ethnic composition, comprising various groups, including Russians, who account for approximately 77%, Tatars, who make up about 3.7%, Ukrainians, who account for about 1.4%, and Bashkirs, who comprise about 1.1%.
How many Russian republics are there?
The Russian Federation, as it exists today, comprises 21 republics, nine territories, 46 regions, one autonomous region, four autonomous districts, and two cities of federal significance.
