10 Jun 2025
9 MIN READ
What is Buryatia?
Summary
Buryatia, or officially the Republic of Buryatia, is a federal subject of the Russian Federation in southeastern Siberia. It is part of the Far Eastern Federal District and lies along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal, the world’s deepest freshwater lake. The geography borders Irkutsk Oblast, Zabaykalsky Krai, and Mongolia to the south. The capital city is Ulan-Ude.
The Republic of Buryatia has a population of just under a million. It was created in 1923 and covers a total area of 135,651 square miles. According to the 2010 national census, there are 461,389 Buryats in the Russian Federation. Along with the Kalmyks, the Buryats speak a Mongolic language.
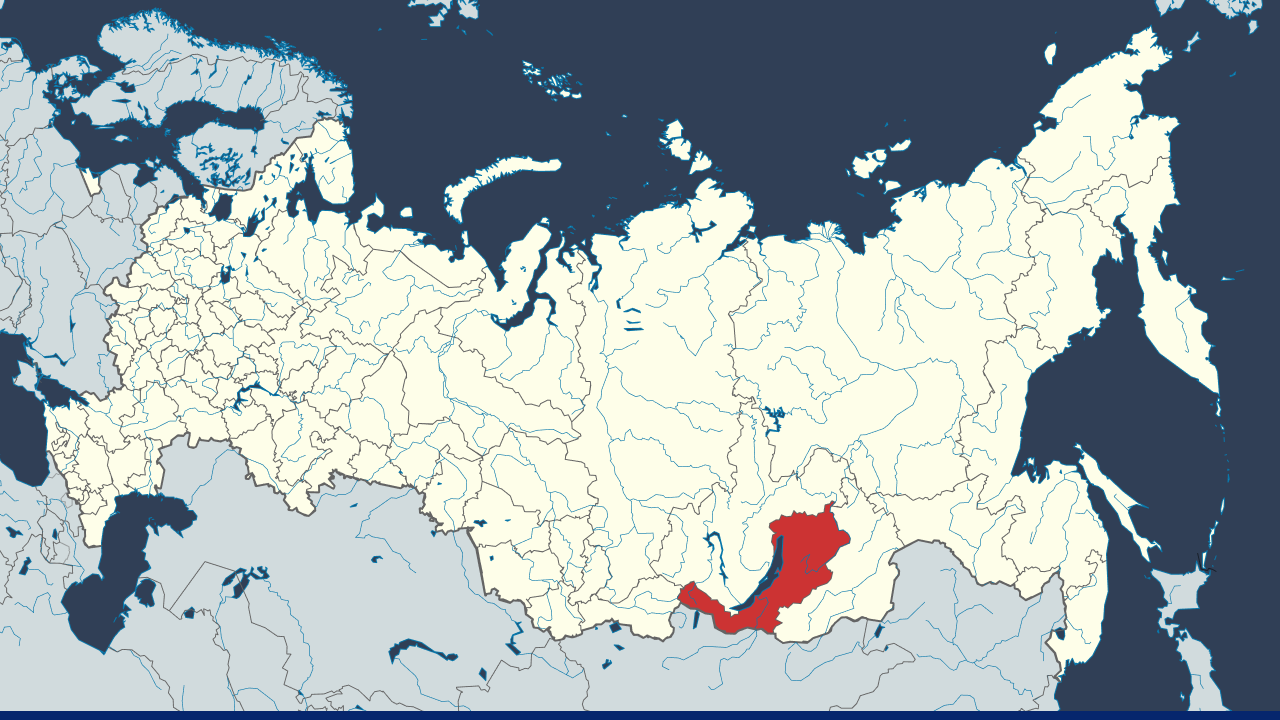
Republic of Buryatia. Source: Wikipedia
What is Lake Baikal? Why is the Heart of the Republic of Buryatia, Russia?
Lake Baikal is Buryatia's biggest treasure and one of the world's most beloved natural wonders. It is considered a sacred place for Buryats and is known as Earth's deepest, oldest, and most voluminous freshwater lake. It is also home to thousands of mostly endemic animal species, such as the Baikal seal.
Lake Baikal has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1996, protected for its unique ecosystem and cultural significance. It significantly contributes to tourism in the Buyat area. Many tourists from other parts of Russia and abroad come to this lake.
What are some interesting activities in Lake Baikal?
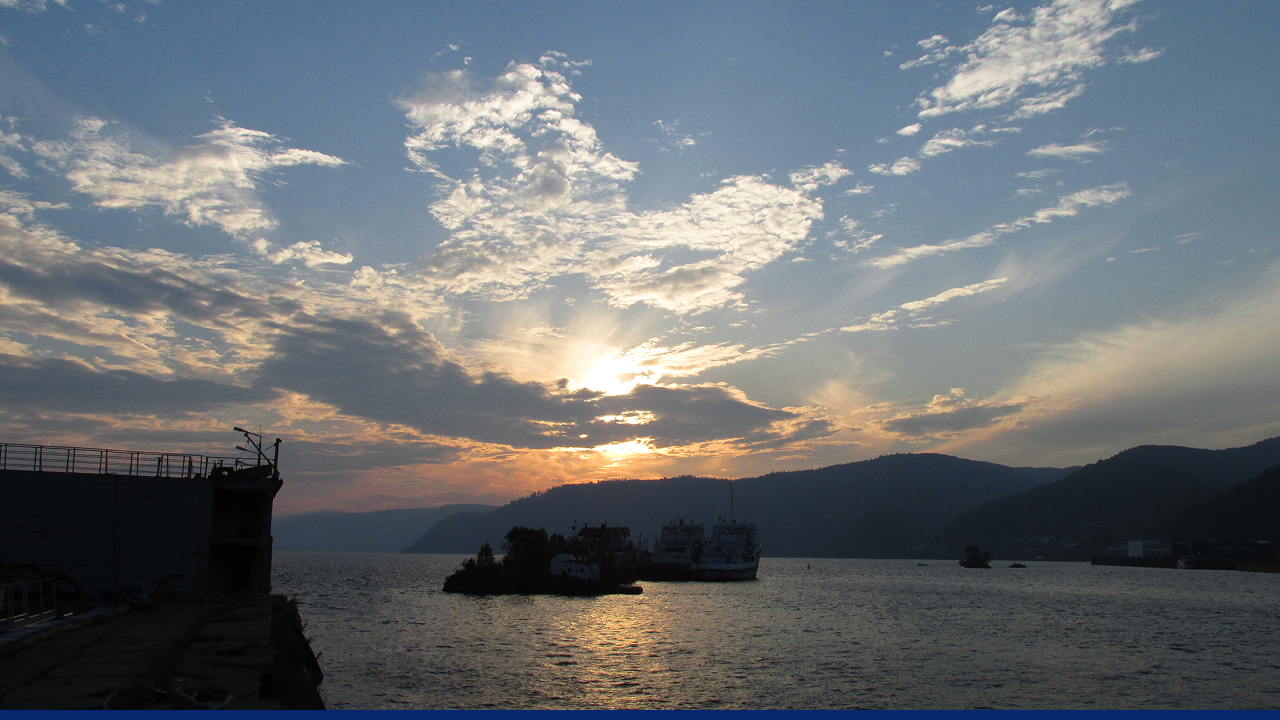

Lake Baikal sunset. Source: Igor Puh
Since it is conveniently next to the Trans-Siberian Railway, many tourists take the opportunity to get out at one of the stops to enjoy the lake. Additionally, the lake is completely frozen over in the winter, allowing for activities such as ice skating, dog sledding, and even driving on the frozen surface.
Ulan-Ude, the capital of the Republic of Buryatia
Ulan-Ude, the capital of the Republic of Buryatia, has a population of just over half a million. It is strategically located at a key stop on the Trans-Siberian railway, which connects Moscow and Vladivostok on the Pacific Ocean. The city is also known as a major Buddhist center in Russia.
One of Buryatia's most famous Buddhist sites is the Ivolginsky Datsan, a monastery located near Ulan-Ude. It attracts pilgrims from across the region. The city is also renowned for having the largest head statue of Vladimir Lenin.
What are the demographics? Who lives in Buryatia, Russia?
In today's times, Buryatia, as a land, has a mix of two-thirds ethnic Russians and 30% Buryats. However, the republic was created as a homeland for Buryats, the land's indigenous people, who also inhabit significant parts of the neighbouring regions, Zabaikalsk Krai and Irkutsk Oblast.
The languages spoken are closely related to Mongolian and share similar traditions and cultures with other Mongolic peoples. The remaining ethnic groups comprise various indigenous and minority groups in Siberia, including the Tatars, Mongols, and Evenks.
What religion is practiced in Buryatia, Russia?
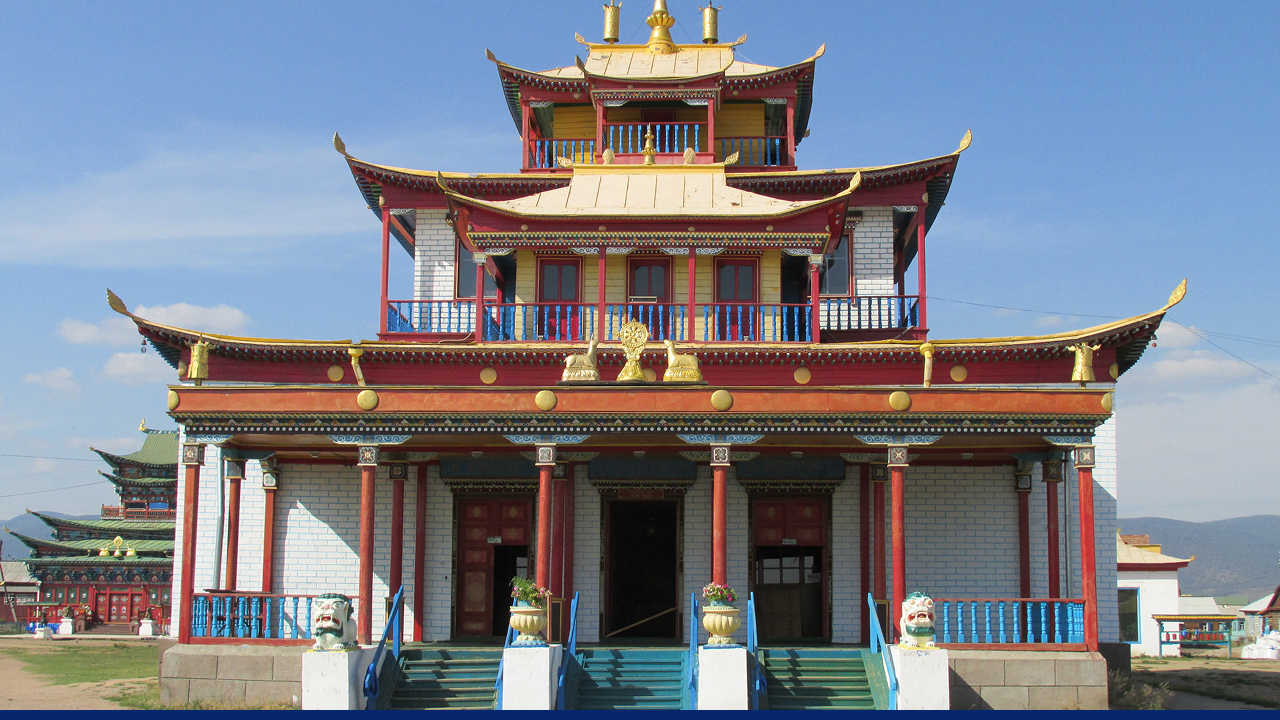

Ivolginsky Datsan monastery in Ulan Ude. Source: Igor Puh
The land is a religious smorgasbord of Buddhism, Russian Orthodoxy, and traditional shamanism. At the same time, a sizable number of people also claim to be irreligious. Along with Tuva and Kalmykia, Buryatia is one of the prominent Buddhist regions in Russia.
Education in Buryatia, Russia
The Russian education system is prevalent in Buryatia. Education is conducted primarily in Russian, although there have been more efforts to conduct education in Buryat or at least promote the language more in schools due to its declining use.
The medium of instruction in native languages and their study has been in sharp decline all over Russia. This is especially after 2017, when Vladimir Putin declared that regional languages as mandatory school subjects are unacceptable, even when they’re official on the republican level.
Development in the education system
At the end of 2024, the Buryat Education Ministry announced that the language of instruction for a quarter of the republic’s schools would be switched to Buryat, beginning in 2026. Many activists welcomed the promise, but others questioned if it was just a way to quiet the nationalist and separatist voices.
Another issue is the rural-urban gap in educational quality; schools in Ulan-Ude are generally better than those in the rest of the region. The government has offered initiatives and plans to improve education, including digital learning, exchange programs, and scholarships.
What are some unusual cultures in Buryatia, Russia?
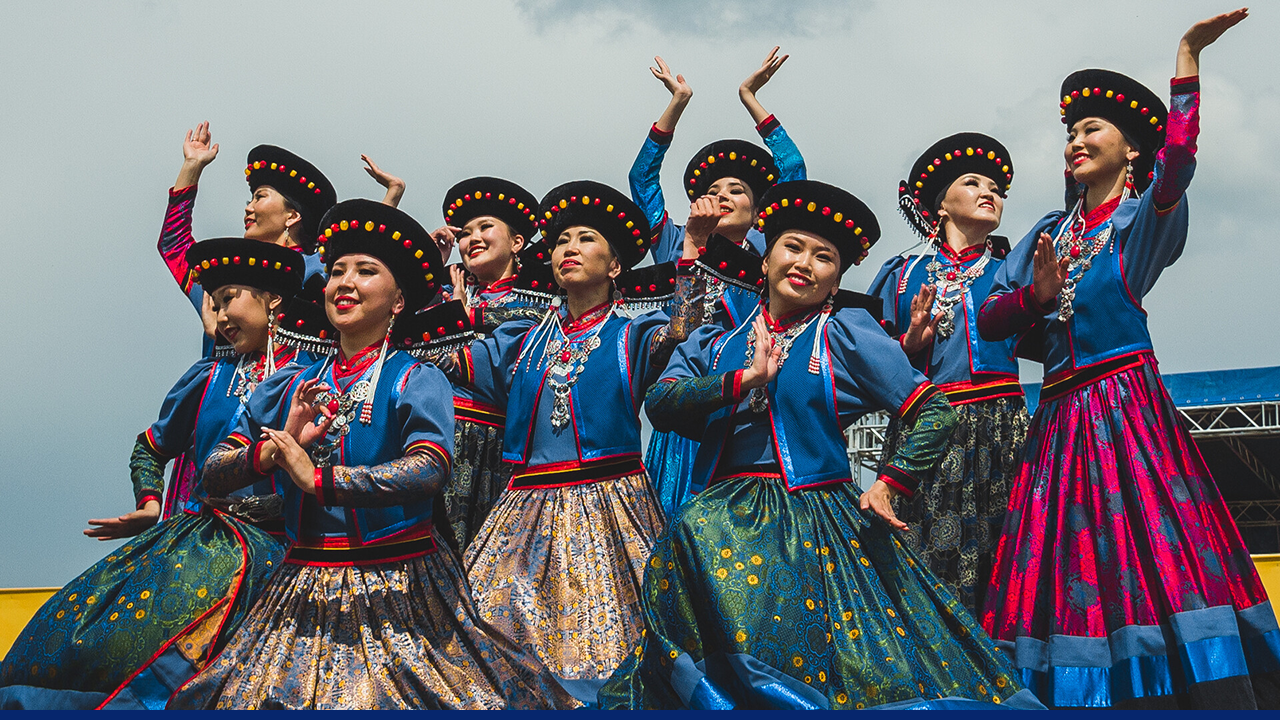

Celebration of Surkharbaan, Buryats' main summer festival. Source: Pavel Kuzmichev, Gateway to Russia
As Buryatia is home to the Buryats, a Mongolic ethnic group. The Buryats' rich cultural heritage blends indigenous traditions with Mongolian and Tibetan Buddhist influences. Buddhism, along with traditional shamanism, plays a central role in Buryat spiritual life. Historically, the Buryats were a nomadic people related to Mongolians.
Hospitality in Buryatia, Russia
Buryat customs emphasize the importance of welcoming guests due to their historic nomadic traditions. The nomadic cultures rely on mutual support and hospitality in the harsh Siberian climate. Generosity is a virtue in these societies.
Guests are often greeted with a milk tea and are often given a silk scarf. Strangers are usually invited in for tea. Unannounced visits in smaller towns and villages are not seen as disrespectful and are welcomed.
What is the Buryat language? How is it a linguistic bridge between Russia and Mongolia?

Central stadium of the Buryat capital. Source: Pavel Kuzmichev, Gateway to Russia
The Buryat language, written in the Mongolian script for centuries, was switched to the Latin alphabet in the 1920s during the Latinization campaign in the Soviet Union, and again to Cyrillic in the 1930s, which remains in use today.
Schools prioritize the Russian language even in areas that are mainly Buryat. Up to 80% of Buryats today don’t speak their mother tongue. As previously mentioned, the education ministry of the Republic of Buryatia is pushing for more use of the language in schools. However, there are speculations that these are empty promises to please many separatist activists.
What is the political landscape in the Republic of Buryatia?
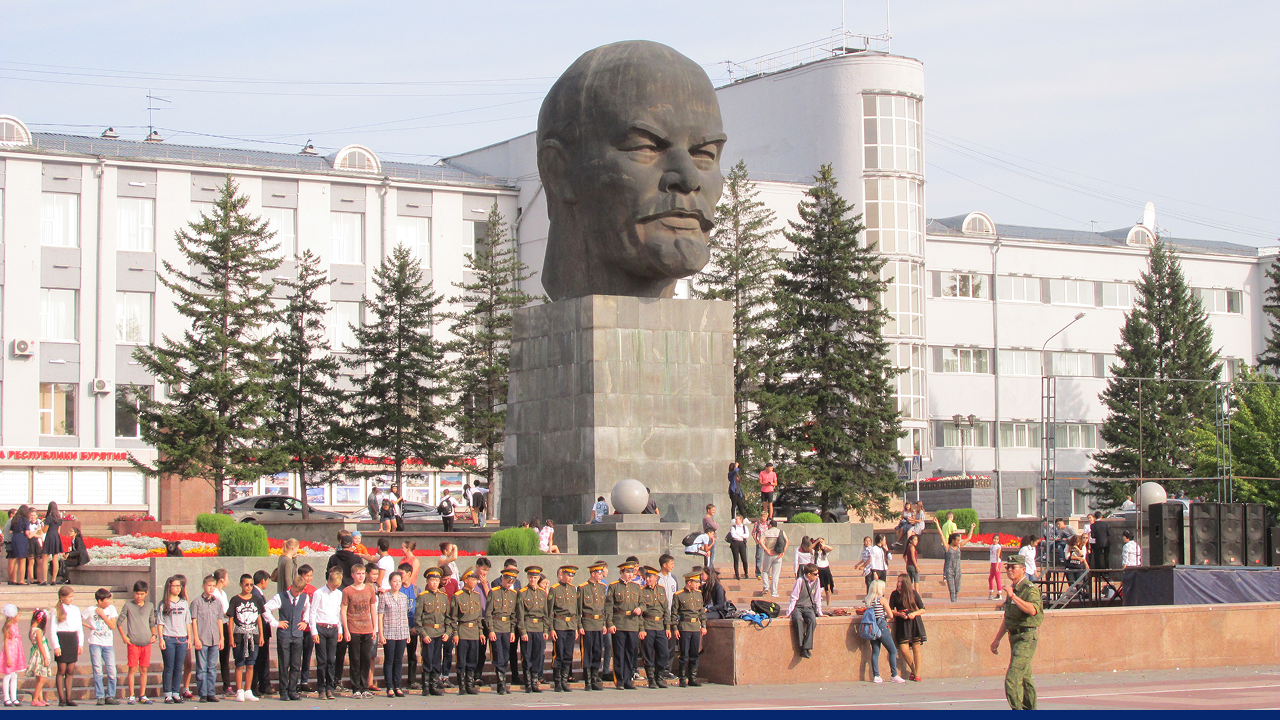

The largest Lenin head statue in Ulan Ude. Source: Igor Puh
Soviet Buryatia: Industrialization and Cultural Suppression
By the 17th century, Buryatia was incorporated into the Russian Empire, which brought about economic development and cultural changes as Russian settlers moved into the region. Under Soviet rule, the Buryat way of life underwent significant alterations.
Under Russian rule, they were forced towards collectivization, industrialization, and the shift from nomadism to agriculture, as well as the suppression of religious practices.
It was in the 50s that the Communist Party tried to separate the Buryats from Mongolia as much as possible, fearing "pan-Mongolian" sentiments. The Buddhist faith also had links to China and Japan, which were geopolitical foes of the Soviet Union.
Post-Soviet Buryatia: between Moscow and local identity

Hills around Buryatia. Source: Igor Puh
Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Buryats have been free to practice their religion again. That doesn’t mean they are free from socio-economic issues. Despite its natural beauty and cultural richness, Buryatia faces economic struggles, including high unemployment and underdeveloped infrastructure.
Many young people leave for larger cities in search of better opportunities. However, they are often discriminated against when they apply for jobs and apartments in cities like Moscow. Many apartment advertisements say, ‘For Slavic tenants only,’ which discriminates against not only Buryats but also other Russians from the East, such as Yakutia and Central Asian migrants.
How is Buryatia’s economy? What are the challenges and opportunities?
Buryatia’s major economic challenge is the dependence on Moscow. Despite its rich natural resources, including up to half of Russia’s zinc reserves, Buryatia remains economically underdeveloped, with high unemployment and low wages.
The region has one of the highest poverty rates in Russia. This has fueled dissatisfaction, leading some Buryats to call for greater autonomy. However, the Russian government heavily suppresses any push for regional independence, which maintains tight control over its federal subjects.
How has the Russia-Ukraine war affected the region?

A protester against Russia's "partial" military mobilization in Ulan-Ude. Source: The Moscow Times
Buryatia has been significantly affected by Russia’s war in Ukraine. The methods of conscription have also not gone without notice. They have been aggressively pulled out of bed in the middle of the night.
The region, which has a sizeable ethnic minority population, has seen a disproportionate number of soldiers sent to the front lines in comparison with areas with more ethnic Russians. This has led to grievances within the local population and increased anti-war sentiment.
An NGO called Free Buryatia was founded in March 2022. The organization advocates for the rights of mobilized Buryats and provides them with legal advice. However, it was banned in Russia in 2023 because it advocated illegal means to avoid military service and attempted to provoke mass separation movements.
Conclusion
Buryatia is an interesting and largely untapped region that bridges Russian and Mongolian cultures, boasting a rich history of traditions and some of the most beautiful natural scenery in Russia. It faces modern challenges as a part of Russia due to institutional discrimination and economic issues, similar to other regions in Russia that are perceived as “less Russian,” such as Tatarstan and Yakutia.
People also ask
Is Buryatia a country?
No, Buryatia is not a country. It is a federal subject of Russia, specifically a republic within the Russian Federation.
Who are the Buryat people in Russia?
The Buryat people are an indigenous Mongolic ethnic group native to Siberia, primarily living in the Republic of Buryatia and surrounding regions in Russia.
What religion is the Buryat Republic?
The Republic of Buryatia does not have an official state religion (as it is part of the Russian Federation, which is constitutionally secular).
What is the meaning of Buryat?
Buryat (also spelled Buriat) refers to the largest indigenous Mongolic people of Siberia, primarily residing in the Republic of Buryatia and its surrounding areas.
When did Russia conquer Buryatia?
Russia began its conquest of Buryatia in the mid-17th century, during the Russian Empire's eastward expansion into Siberia.
